Potential risks include the creation of dangerous variants and mutagenicity, carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, and embryotoxicity Chamod, Hadj Hassine, Huntsman, Marikawa, Standing, Swanstrom, Waters, Zhou, Zibat. Multiple analyses have identified variants potentially created by molnupiravir Fountain-Jones, Kosakovsky Pond, Sanderson, twitter.com. There is substantial publication bias. Multiple trials have not reported results and did not respond to requests Lawrence.
Recent:Amani Fountain-Jones Schreiber Standing Cheng Chen Yoshida.
Molnupiravir has been officially adopted
in 30 countries.
Submit updates/corrections .
Apr 23 |
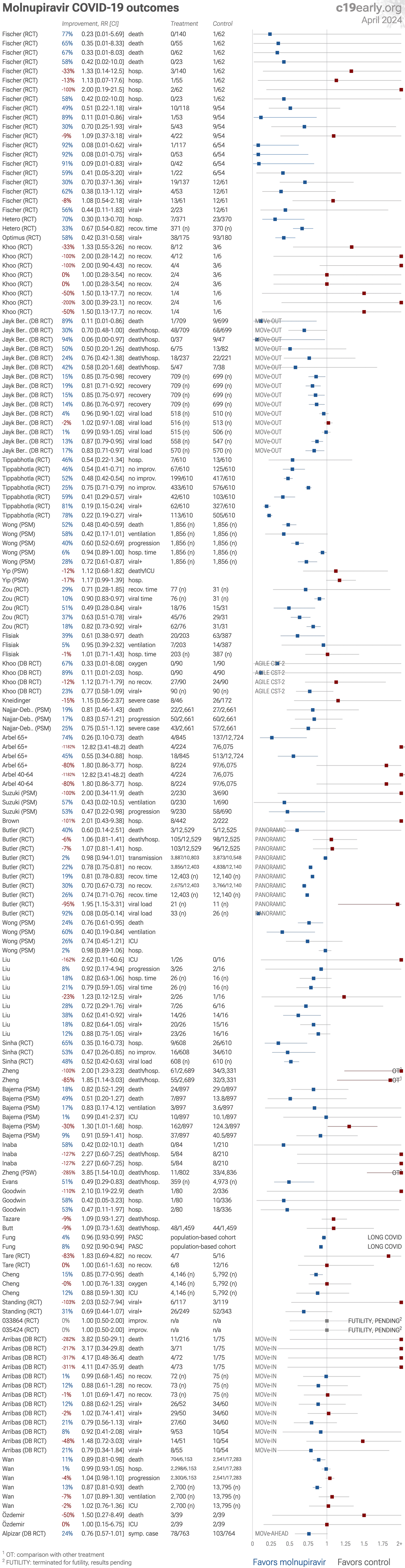
et al., Immunity, Inflammation and Disease, doi:10.1002/iid3.1262 | Comparison of effectiveness and safety of molnupiravir versus sotrovimab for COVID‐19: A systematic review and meta‐analysis |
| Meta analysis of 13 studies involving 16,166 patients showing higher mortality and higher incidence of adverse events with molnupiravir compared with sotrovimab. | ||
Mar 25 |
et al., Celal Bayar Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Enstitüsü Dergisi, doi:10.34087/cbusbed.1423523 | COVID-19 enfeksi̇yonunda molnupiravi̇r tedavi̇si̇ alan hastalarin değerlendi̇ri̇lmesi̇ |
| 50% higher mortality (p=1) and no change in ICU admission (p=1). Retrospective study of 78 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Turkey showing no significant difference in mortality or discharge rates with molnupiravir treatment. | ||
Mar 22 |
et al., The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2 | Effect of molnupiravir on SARS-CoV-2 evolution in immunocompromised patients: a retrospective observational study |
| Analysis of immunocompromised COVID-19 showing rapid creation of new variants with molnupiravir. Some mutations became fixed in the viral population and the distinctive mutational pattern, dominated by G-to-A and C-to-T transitions, persi.. | ||
Mar 2 |
et al., Antiviral Research, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2024.105840 | The host-targeted antiviral drug Zapnometinib exhibits a high barrier to the development of SARS-CoV-2 resistance |
| In Vitro study showing that molnupiravir and paxlovid induced resistant variants in SARS-CoV-2 during serial passaging, while the host-directed antiviral zapnometinib did not. Authors found that molnupiravir did not lead to abrogated vira.. | ||
Feb 23 |
et al., Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-024-45641-0 | Randomized controlled trial of molnupiravir SARS-CoV-2 viral and antibody response in at-risk adult outpatients |
| 103% worse viral clearance (p=0.33). PANORAMIC virology-sub-study showing increased viral persistence with molnupiravir treatment. Molnupiravir 800mg twice daily for 5 days led to faster initial viral decline but 86% still had detectable virus by day 5. By day 14, molnupirav.. | ||
Feb 9 |
et al., Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-53862-y | Comparison of azvudine, molnupiravir, and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in adult patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study |
| Retrospective 157 hospitalized mild-to-moderate COVID-19 patients showing no significant differences between azvudine, molnupiravir, and paxlovid for time to viral clearance and length of hospitalization. | ||
Feb 9 |
et al., Kidney International Reports, doi:10.1016/j.ekir.2024.02.009 | Effectiveness of molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in CKD patients with COVID-19 |
| 15% lower mortality (p=0.003), no change in oxygen therapy (p=1), and 12% lower ICU admission (p=0.52). Retrospective emulated target trial of hospitalized COVID-19 patients with chronic kidney disease in Hong Kong showing lower mortality with molnupiravir and paxlovid treatment. No significant reduction was found in ICU admission or ventil.. | ||
Feb 6 |
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-3899998/v1 | Real-world Efficacy of Ensitrelvir in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19 in Japan: A Retrospective Observational Study |
| Retrospective 154 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Japan showing faster viral clearance and shorter hospitalization with ensitrelvir treatment compared to remdesivir or molnupiravir. There was no significant difference for fever resoluti.. | ||
Jan 26 |
et al., JAMA Health Forum, doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2023.5044 | Clinical Risk and Outpatient Therapy Utilization for COVID-19 in the Medicare Population |
| Analysis of Medicare beneficiaries in 2022 showing that outpatient COVID-19 treatments like antivirals and monoclonal antibodies were disproportionately used by patients at lower risk of severe infection and outcomes. Retrospective studie.. | ||
Jan 24 |
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-3876022/v1 | Oral antivirals for COVID-19 among patients with cancer |
| Retrospective 67 cancer outpatients treated with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir or molnupiravir, compared to 56 untreated concurrent controls, reporting lower mortality with treatment. However, Figure 3 shows the opposite results for invasive mec.. | ||
Jan 4 |
et al., Virus Evolution, doi:10.1093/ve/veae001 | Genetic consequences of effective and suboptimal dosing with mutagenic drugs in a hamster model of SARS-CoV-2 infection |
| Syrian hamster study showing that short-term treatment with the mutagenic antiviral drugs favipiravir and molnupiravir led to increased genetic variation in SARS-CoV-2 viral populations. Treatment with effective antiviral doses resulted i.. | ||
Dec 28 2023 |
et al., Asian Medical Journal and Alternative Medicine, 23:3 | Molnupiravir Metabolite--N4-hydroxycytidine Causes Cytotoxicity and DNA Damage in Mammalian Cells in vitro: N4-hydroxycytidine Induced Cytotoxicity DNA Damage |
| In Vitro study showing concentration-dependent cytotoxicity and DNA damage in human skin and lung cell lines with NHC, the active metabolite of molnupiravir, at concentrations spanning the therapeutic range. The genotoxic effects raise co.. | ||
Dec 6 2023 |
et al., Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1287542 | Unveiling patenting strategies of therapeutics and vaccines: evergreening in the context of COVID-19 pandemic |
| Review of the patenting activity and evergreening approaches for three major COVID-19 antiviral medications – remdesivir, molnupiravir, and favipiravir. Authors found extensive primary and secondary patent filing, with 29 applications cov.. | ||
Nov 30 2023 |
et al., Clinical Interventions in Aging, doi:10.2147/cia.s431271 | Factors Affecting Mortality in Elderly Hypertensive Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Retrospective Study |
| 232% higher mortality (p=0.006). Retrospective 748 elderly hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China showing increased risk of death with paxlovid/molnupiravir. Multivariate analysis showed that paxlovid/molnupiravir was independently associated with higher in-hospital mor.. | ||
Nov 23 2023 |
et al., Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-023-00891-1 | Virologic Outcomes with Molnupiravir in Non-hospitalized Adult Patients with COVID-19 from the Randomized, Placebo-Controlled MOVe-OUT Trial |
| Virological outcomes for the MOVe-OUT trial. Results are shown with the main paper [Jayk Bernal]. | ||
Nov 22 2023 |
et al., Infection & Chemotherapy, doi:10.3947/ic.2023.0087 | Effectiveness of Molnupiravir Treatment in Patients with COVID-19 in Korea: A Propensity Score Matched Study |
| 25% lower mortality (p<0.0001) and 29% lower progression (p<0.0001). PSM retrospective 190,692 COVID-19 patients treated with molnupiravir and 762,768 matched controls, showing lower mortality and combined severe/critical illness and mortality with treatment. | ||
Nov 20 2023 |
et al., BJGP Open, doi:10.3399/bjgpo.2023.0109 | The DAWN antivirals trial: process evaluation of a COVID-19 trial in general practice |
| 83% worse recovery (p=0.36). Very small early terminated RCT with 8 molnupiravir and 17 placebo patients showing worse recovery with molnupiravir, without statistical significance. | ||
Nov 11 2023 |
et al., Nucleic Acids Research, doi:10.1093/nar/gkad1002 | Uridine–cytidine kinase 2 potentiates the mutagenic influence of the antiviral β-d-N4-hydroxycytidine |
| In Vitro study showing that molnupiravir increased mutation rates in mouse blood cancer cell lines. The mutagenic effects were enhanced by overexpression of the enzyme uridine-cytidine kinase 2 (Uck2), and lessened in Uck2 knockout cells... | ||
Oct 31 2023 |
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-3484296/v1 | Liver injury in non-severe COVID-19 with various pandemic phases: a real-world study |
| Prospective study of 300 patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 in Thailand, showing the highest risk of liver injury with molnupiravir treatment, OR 3.4 (p = 0.06). | ||
Oct 24 2023 |
et al., Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-023-03248-3 | Anti-COVID drug accelerates viral evolution |
| Discussion of the creation of new COVID-19 variants via treatment with molnupiravir. Sanderson et al. [Sanderson] showed that thousands of viruses with many mutations - sometimes more than 100 - survived molnupiravir treatment, and that m.. | ||
Oct 23 2023 |
et al., JAMA Internal Medicine, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2023.5099 | Nirmatrelvir and Molnupiravir and Post–COVID-19 Condition in Older Patients |
| 4% lower PASC (p=0.001). Retrospective 8,089 molnupiravir patients in the USA showing a small reduction in long COVID with treatment. Confounding is likely significant as below, and may eliminate the benefit. Results specific to the COVID-19 code should be closer.. | ||
Sep 25 2023 |
et al., Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6 | A molnupiravir-associated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes |
| Identification of SARS-CoV-2 variants created by molnupiravir treatment, including cases of onwards transmission. Authors find a class of long phylogenetic branches almost exclusively matching the time period, location, and age groups of .. | ||
Sep 23 2023 |
et al., Reproductive Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2023.108475 | An active metabolite of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir impairs mouse preimplantation embryos at clinically relevant concentrations |
| Analysis of molnupiravir active metabolite N4-hydroxycytidine's effects on mouse preimplantation embryos in vitro, showing embryotoxicity at clinically relevant concentrations. The researchers found that N4-hydroxycytidine impaired blasto.. | ||
Sep 8 2023 |
et al., Journal of Infection, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2023.08.016 | Molnupiravir for Intra-Household Prevention of COVID-19: the MOVe-AHEAD Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial |
| 24% fewer symptomatic cases (p=0.06). PEP RCT 1,527 patients showing lower COVID-19 cases with molnupiravir, without statistical significance. | ||
Aug 31 2023 |
et al., iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.107786 | N4-hydroxycytidine, the active compound of Molnupiravir, promotes SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis and escape from a neutralizing nanobody |
| In Vitro study showing that NHC, the active compound molnupiravir, can promote rapid selection of immune escape mutants. NHC treatment enabled selection of nanobody-resistant mutants much faster than without NHC. While an in vitro model w.. | ||
Aug 7 2023 |
et al., BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2022-069176 | Platform adaptive trial of novel antivirals for early treatment of COVID-19 In the community (PANORAMIC): protocol for a randomised, controlled, open-label, adaptive platform trial of community novel antiviral treatment of COVID-19 in people at increased risk of more severe disease |
| PANORAMIC protocol paper, published over 9 months after publication of the molnupiravir arm [Butler]. | ||
Aug 7 2023 |
et al., Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2023.109865 | Molnupiravir, a ribonucleoside antiviral prodrug against SARS-CoV-2, alters the voltage-gated sodium current and causes adverse events |
| In vitro study showing that molnupiravir inhibited sodium channel currents by altering channel gating kinetics, which may explain some of the neurological and gastrointestinal side effects. | ||
Jul 19 2023 |
et al., Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciad409 | Impact of Molnupiravir Treatment on Patient-Reported Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Symptoms in the Phase 3 MOVe-OUT Trial: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial |
| Symptom recovery details for the MOVe-OUT trial. Results are shown with the main paper [Jayk Bernal]. | ||
Jun 1 2023 |
et al., The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiad195 | Molnupiravir Use and 30-Day Hospitalizations or Death in Previously Uninfected Non-hospitalized High-risk Population with COVID-19 |
| 9% higher combined mortality/hospitalization (p=0.75). Retrospective 65,010 veterans in the USA, showing no significant difference in hospitalization/death with molnupiravir treatment. 1,729 patients received molnupiravir. Authors emulate a target trial closely matching the MOVe-OUT RCT and u.. | ||
May 16 2023 |
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.05.12.23289914 | Effectiveness of Sotrovimab and Molnupiravir in community settings in England across the Omicron BA.1 and BA.2 sublineages: emulated target trials using the OpenSAFELY platform |
| 9% higher combined mortality/hospitalization (p=0.28). OpenSAFELY retrospective 75,048 outpatients in the UK, using the clone-censor-weight approach to address immortal time bias, showing no significant difference in combined mortality/hospitalization with molnupiravir treatment. | ||
May 10 2023 |
et al., Elsevier BV, doi:10.2139/ssrn.4444431 | Real-Life Comparison of Mortality in Non-Hospitalised Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection at Risk for Clinical Progression Treated with Molnupiravir or Nirmatrevir Plus Ritonavir During the Omicron Era in Italy: A Nationwide, Observational Study |
| 47% higher mortality (p=0.0001). Prospective study of 17,977 outpatients treated with molnupiravir and 11,576 treated with paxlovid, showing significant mortality with both treatments, and lower mortality with paxlovid. | ||
Apr 30 2023 |
et al., Annals of Internal Medicine, doi:10.7326/M22-3057 | Effectiveness of Molnupiravir and Nirmatrelvir–Ritonavir in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 |
| 13% lower mortality (p<0.0001), 7% higher ventilation (p=0.49), and 2% higher ICU admission (p=0.9). Target trial emulation retrospective with 16,495 patients in Hong Kong, showing lower mortality with molnupiravir, but no significant difference for ventilation and ICU admission. See also [acpjournals.org], [acpjournals.org]. | ||
Mar 15 2023 |
et al., PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0281915 | Evaluation of outpatient treatment for non-hospitalised patients with COVID-19: The experience of a regional centre in the UK |
| 110% higher mortality (p=0.47) and 58% lower hospitalization (p=0.7). Retrospective 604 outpatients in the UK, showing lower risk of hospitalization with molnupiravir treatment, without statistical significance due to the small number of hospitalizations. | ||
Feb 24 2023 |
Refusal of the marketing authorisation for Lagevrio (molnupiravir) | |
| The European Medicines Agency has recommended the refusal of the marketing authorisation of molnupiravir. | ||
Feb 22 2023 |
et al., Journal of Infection, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029 | Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir reduce mortality risk during post-acute COVID-19 phase |
| 11% lower mortality (p=0.02), 1% lower hospitalization (p=0.76), and 4% higher progression (p=0.18). Retrospective 30,040 hospitalized patients in Hong Kong, showing lower mortality with molnupiravir treatment. | ||
Feb 21 2023 |
, Press Release | Merck Provides Update on Phase 3 MOVe-AHEAD Trial Evaluating LAGEVRIO™ (molnupiravir) for Post-exposure Prophylaxis for Prevention of COVID-19 |
| MOVe-AHEAD PEP RCT reporting no significant difference in cases. Limited information is available. There were 23.6% fewer cases with treatment, but the number of cases and confidence interval are not provided. | ||
Feb 1 2023 |
, R., Science, doi:10.1126/science.adg9677 | Could a popular COVID-19 antiviral supercharge the pandemic? |
| Coverage of [Fountain-Jones, Sanderson] which show evidence for molnupiravir creating new variants. The quote "Right now, it’s much ado about nothing" is from Emory University, where Molnupiravir was invented.. | ||
Jan 25 2023 |
et al., Journal of Infection, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.012 | Real-world effectiveness of molnupiravir, nirmatrelvir-ritonavir, and sotrovimab on preventing hospital admission among higher-risk patients with COVID-19 in Wales: A retrospective cohort study |
| 51% lower combined mortality/hospitalization (p=0.008). Retrospective high risk outpatients in the UK, showing lower hospitalization/death with molnupiravir treatment. Residual confounding is likely with adjustments having no detail on specific comorbidities. | ||
Jan 22 2023 |
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.01.20.23284849 | Comparative effectiveness of Paxlovid versus sotrovimab and molnupiravir for preventing severe COVID-19 outcomes in non-hospitalised patients: observational cohort study using the OpenSAFELY platform |
| 285% higher combined mortality/hospitalization (p=0.004). OpenSAFELY retrospective 5,638 outpatients in the UK, showing significantly higher hospitalization/death for molnupiravir compared with paxlovid. | ||
Jan 15 2023 |
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-2451986/v1 | Real-world data concerning the efficacy of molnupiravir in patients vaccinated against COVID-19 during the Omicron surge in Japan |
| 127% higher combined mortality/hospitalization (p=0.22) and 127% higher hospitalization (p=0.22). Retrospective 294 consecutive patients in Japan, showing higher risk of hospitalization/death with molnupiravir, without statistical significance. | ||
Dec 21 2022 |
et al., Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm12010034 | Safety Profile of Molnupiravir in the Treatment of COVID-19: A Descriptive Study Based on FAERS Data |
| Safety analysis of molnupiravir reporting an unexpectedly high rate of serious adverse reactions. | ||
Dec 6 2022 |
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.12.05.22283134 | Effectiveness of COVID-19 treatment with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir or molnupiravir among U.S. Veterans: target trial emulation studies with one-month and six-month outcomes |
| 18% lower mortality (p=0.4), 1% lower ICU admission (p=1), and 30% higher hospitalization (p=0.04). Retrospective 112,380 high-risk patients in the USA, showing significantly higher acute or long-term care admission at 180 days with molnupiravir treatment, and no significant difference for other outcomes. The title and headers of Table .. | ||
Nov 16 2022 |
et al., BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj-2022-071932 | Comparative effectiveness of sotrovimab and molnupiravir for prevention of severe covid-19 outcomes in patients in the community: observational cohort study with the OpenSAFELY platform |
| 100% higher combined mortality/hospitalization (p=0.005). Retrospective 3,331 sotrovimab and 2,689 molnupiravir patients in the UK, showing higher risk of combined hospitalization/death with molnupiravir. | ||
Nov 14 2022 |
et al., Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.31508 | Efficacy and Safety of Molnupiravir in Mild COVID-19 Patients in India |
| 65% lower hospitalization (p=0.005), 53% greater improvement (p=0.01), and 48% improved viral clearance (p<0.0001). RCT 1,218 outpatients in India, showing lower hospitalization, better clinical improvement, and improved viral clearance with molnupiravir. | ||
Oct 30 2022 |
et al., Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-022-00716-7 | Disease Progression of Hospitalized Elderly Patients with Omicron BA.2 Treated with Molnupiravir |
| 18% shorter hospitalization (p=0.14) and 21% faster viral clearance (p=0.1). Retrospective 42 elderly patients in China showing faster viral clearance with molnupiravir. | ||
Oct 8 2022 |
et al., The Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01586-0 | Real-world effectiveness of molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir against mortality, hospitalisation, and in-hospital outcomes among community-dwelling, ambulatory patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection during the omicron wave in Hong Kong: an observational study |
| 24% lower mortality (p=0.01), 60% lower ventilation (p=0.02), 26% lower ICU admission (p=0.24), and 2% lower hospitalization (p=0.58). PSM retrospective 1,074,856 outpatients in Hong Kong, showing lower mortality with molnupiravir. | ||
Oct 6 2022 |
et al., The Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1 (date from preprint) | Molnupiravir plus usual care versus usual care alone as early treatment for adults with COVID-19 at increased risk of adverse outcomes (PANORAMIC): an open-label, platform-adaptive randomised controlled trial |
| 6% higher combined mortality/hospitalization (p=0.69), 7% higher hospitalization (p=0.67), 2% lower transmission (p=0.88), and 22% improved recovery (p<0.0001). 26,411 patient RCT in the UK, showing faster recovery but no significant difference in hospitalization/death or transmission. Improved recovery may be in part due to the open label design with self-reported symptomatic data. Viral load in.. | ||
Oct 6 2022 |
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-2105569/v1 | Genomic Evolution of Sars-Cov-2 in Molnupiravir-Treated Patients Compared to Paxlovid-Treated and Drug-Naïve Patients: A Proof-of-Concept Study |
| Mutation analysis showing over 5x greater within-host genetic diversity with molnupiravir compared to paxlovid or no treatment. | ||
Oct 6 2022 |
et al., Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofac527 | Demographics and outcomes of initial phase of COVID-19 Medicines Delivery Units across 4 UK centres during peak B1.1.529 omicron epidemic: a service evaluation |
| 101% higher hospitalization (p=0.51). Retrospective 442 patients in the UK treated with molnupiravir, and 222 eligible but declining treatment, showing no significant difference in hospitalization. No group details are provided and the results are subject to confounding by in.. | ||
Oct 5 2022 |
et al., Clinical and Experimental Medicine, doi:10.1007/s10238-022-00949-3 (date from preprint) | Real-world clinical outcomes of treatment with molnupiravir for patients with mild-to-moderate coronavirus disease 2019 during the Omicron variant pandemic |
| 53% lower progression (p=0.04). Retrospective 1,921 patients in Japan, showing lower progression with molnupiravir use. | ||
Oct 1 2022 |
et al., Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, doi:10.1002/em.22510 | Evaluation of the mutagenic effects of Molnupiravir and N4-hydroxycytidine in bacterial and mammalian cells by HiFi sequencing |
| In Vitro genotoxocity study of molnupiravir showing dose dependent increased genome-wide mutation frequencies with mouse lymphoma L5178Y and human lymphoblastoid TK6 cells. | ||
Sep 29 2022 |
et al., New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2204919 (date from preprint) | Molnupiravir Use and Severe Covid-19 Outcomes During the Omicron Surge |
| 74% lower mortality (p=0.008) and 45% lower hospitalization (p=0.01). Retrospective 19,868 patients eligible for molnupiravir treatment in Israel with 1,069 treated, showing lower mortality and hospitalization with treatment for the subgroup of patients ≥65, and higher mortality for patients 40-64. Authors .. | ||
Sep 20 2022 |
et al., Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac781 | Effectiveness of Molnupiravir in High Risk Patients: a Propensity Score Matched Analysis |
| 19% lower mortality (p=0.48), 17% lower progression (p=0.34), and 25% lower severe cases (p=0.15). PSM retrospective 2,661 molnupiravir patients in Israel, showing lower mortality and severe COVID-19, without statistical significance. Significant benefit was seen in some subgroups, and significant harm was seen in the <75 subgroup. | ||
Sep 9 2022 |
et al., Infection, doi:10.1007/s15010-022-01914-8 | Outcome of lung transplant recipients infected with SARS-CoV-2/Omicron/B.1.1.529: a Nationwide German study |
| 15% higher severe cases (p=0.71). Retrospective 218 COVID+ lung transplant patients in Germany, showing no significant difference in severe cases with early molnupiravir use. | ||
Aug 2 2022 |
et al., Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, doi:10.1093/jac/dkac440 (date from preprint) | Evaluation of publication bias for 12 clinical trials of molnupiravir to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection in 13,694 patients with meta-analysis |
| Meta analysis of molnupiravir trials showing 12 registered RCTs in India with only one presented at a conference, and two issuing press releases suggesting failure. Authors find that ~90% of the global data on molnupiravir has not been pu.. | ||
Jul 29 2022 |
et al., Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-022-32045-1 | SARS-CoV-2 VOC type and biological sex affect molnupiravir efficacy in severe COVID-19 dwarf hamster model |
| Roborovski dwarf hamster and in vitro study finding molnupiravir efficacy varied significantly by SARS-CoV-2 variant in the hamster model, in contrast to no significant difference seen in cultured cells and human organoids. Efficacy for o.. | ||
Jul 24 2022 |
et al., The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00644-2 (date from preprint) | Molnupiravir versus placebo in unvaccinated and vaccinated patients with early SARS-CoV-2 infection in the UK (AGILE CST-2): a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 2 trial |
| 89% lower hospitalization (p=0.12), 12% worse recovery (p=0.74), and 23% improved viral clearance (p=0.07). RCT 90 molnupiravir and 90 placebo patients, showing faster viral clearance with treatment, not reaching the pre-defined threshold for superiority and recommendation as a candidate for large scale evaluation. | ||
Jul 6 2022 |
et al., Pharmacological Reports, doi:10.1007/s43440-022-00408-6 (date from preprint) | Real-world experience with molnupiravir during the period of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant dominance |
| 39% lower mortality (p=0.03), 5% lower ventilation (p=1), and 1% longer hospitalization (p=0.97). Retrospective 590 patients in Poland, 203 treated with mulnupiravir, showing lower mortality with treatment. | ||
Jun 15 2022 |
et al., Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.939573 | Antiviral Efficacy and Safety of Molnupiravir Against Omicron Variant Infection: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial |
| 29% faster recovery (p=0.5) and 10% faster viral clearance (p=0.009). RCT 116 mild/moderate COVID-19 patients in China, showing improved viral clearance with treatment. | ||
May 24 2022 |
et al., Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac687 (date from preprint) | Impact of the use of oral antiviral agents on the risk of hospitalization in community COVID-19 patients |
| 12% higher combined mortality/ICU admission (p=0.66) and 17% higher hospitalization (p=0.06). Propensity score weighted retrospective of 93,883 outpatients in Hong Kong, 5,808 treated with molnupiravir and 4,921 treated with paxlovid, showing higher hospitalization and higher combined mortality/mechanical ventilation/ICU admission.. | ||
May 20 2022 |
et al., The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2 (date from preprint) | Real-world effectiveness of early molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 without supplemental oxygen requirement on admission during Hong Kong's omicron BA.2 wave: a retrospective cohort study |
| 52% lower mortality (p<0.0001), 58% lower ventilation (p=0.06), 40% lower progression (p<0.0001), and 6% shorter hospitalization (p=0.03). PSM retrospective 40,776 patients in Hong Kong, showing lower mortality and lower combined mortality, ventilation, ICU, and oxygen therapy with molnupiravir treatment. | ||
May 17 2022 |
et al., JCI Insight, doi:10.1172/jci.insight.160108 | Molnupiravir inhibits SARS-CoV-2 variants including Omicron in the hamster model |
| Syrian hamster study showing efficacy of molnupiravir for multiple variants including omicron. | ||
Apr 18 2022 |
et al., Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14040841 | Lethal Mutagenesis of RNA Viruses and Approved Drugs with Antiviral Mutagenic Activity |
| Review of lethal mutagenesis for RNA viruses, as used by molnupiravir, favipiravir, and ribavirin. Authors note the potential for permanently modifying the genomes of patients while causing teratogenicity or embryotoxicity, and the potent.. | ||
Apr 8 2022 |
, T. | PANORAMIC recruitment analysis |
| Analysis of the PANORAMIC trial recuitment suggesting that if the trial shows efficacy, the NNT will be >200. | ||
Mar 11 2022 |
et al., The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, doi:10.4269/ajtmh.21-1339 | Making Statistical Sense of the Molnupiravir MOVe-OUT Clinical Trial |
| Discussion of concerns with the MOVe-OUT trial, including the reversal of the treatment effect post-interim analysis. | ||
Feb 24 2022 |
et al., SSRN Electronic Journal, doi:10.2139/ssrn.4042673 | Efficacy and Safety of Molnupiravir for the Treatment of Non-Hospitalized Adults With Mild COVID-19: A Randomized, Open-Label, Parallel-Group Phase 3 Trial |
| 46% lower hospitalization (p=0.26), 46% greater improvement (p<0.0001), and 59% improved viral clearance (p<0.0001). RCT 1,220 patients in India, showing lower risk of hospitalization and improved recovery with treatment. CTRI/2021/07/034588. | ||
Feb 3 2022 |
et al., Science, doi:10.1126/science.abn0048 | Lethal mutagenesis as an antiviral strategy |
| Review of the unknown long-term cancer, reproductive, and escape variant creation risks of molnupiravir. For more discussion see [twitter.com, twitter.com, twitter.com]. | ||
Jan 28 2022 |
et al., Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, doi:10.1002/em.22471 | Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir |
| Review of antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis, including molnupiravir and favipiravir, and the potential mutagenic risks to human DNA and human mitochondrial DNA. Author recommends monitoring for mutagenicity,.. | ||
Dec 16 2021 |
et al., NEJM Evidence, doi:10.1056/EVIDoa2100044 | Randomized Trial of Molnupiravir or Placebo in Patients Hospitalized with Covid-19 |
| 282% higher mortality (p=0.31), 1% improved recovery (p=0.96), and 12% improved viral clearance (p=0.57). RCT 304 hospitalized patients, 218 treated with molnupiravir, showing no significant differences. MOVe-IN MK-4482-001. NCT04575584. | ||
Dec 16 2021 |
et al., New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2116044 | Molnupiravir for Oral Treatment of Covid-19 in Nonhospitalized Patients |
| 89% lower mortality (p=0.01), 30% lower combined mortality/hospitalization (p=0.05), 15% faster recovery (p=0.02), and 4% improved viral clearance (p=0.2). MOVe-OUT RCT, showing significantly lower risk of hospitalization or death. In subgroup analysis efficacy was much lower with the delta variant. See also [Guan, Strizki]. Discussion of concerns with this trial can be found at [defyccc.com.. | ||
Dec 3 2021 |
, Authorea, doi:10.22541/au.163854323.34557301/v1 | Treating a Pandemic Respiratory Disease with a Mutagen is a Doomsday Scenario |
| Review of molnupiravir's mutagenic mechanism of action, and analysis of the increased probability of creating dangerous variants. | ||
Nov 6 2021 |
, L., TrialSite News | Molnupiravir: mutagenic, carcinogenic, authorized in the UK |
| Discussion of concerns with molnupiravir and the MOVe-OUT trial. Author notes that results showing bone marrow toxicity in dogs were mentioned in this preprint [medrxiv.org], but removed from the journal version [journals.asm.org]. Some a.. | ||
Oct 9 2021 |
Two Indian drugmakers to end trials of generic Merck pill for moderate COVID-19 | |
| no change in recovery (p=1). Trial CTRI/2021/08/035424 for moderate condition patients has been reported as terminated for futility. Results are not available yet [trialsearch.who.int]. | ||
Oct 9 2021 |
Two Indian drugmakers to end trials of generic Merck pill for moderate COVID-19 | |
| no change in recovery (p=1). Trial CTRI/2021/05/033864 for moderate condition patients has been reported as terminated for futility. Results are not available yet [trialsearch.who.int]. | ||
Sep 13 2021 |
et al., Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, doi:10.1038/s41594-021-00657-8 | Molnupiravir: coding for catastrophe |
| Review of recent studies on molnupiravir's mechanism of lethal mutagenesis. Authors note that potential off-target effects require further investigation, because molnupiravir may be mutagenic to host DNA during host DNA replication. | ||
Aug 27 2021 |
et al., Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, doi:10.1093/jac/dkab318 | Optimal dose and safety of molnupiravir in patients with early SARS-CoV-2: a Phase I, open-label, dose-escalating, randomized controlled study |
| 33% worse recovery (p=0.63). Dose and safety study of molnupiravir with 18 participants, finding no serious adverse events in short-term followup. There was no significant difference in clinical outcomes. NCT04746183. | ||
Jul 21 2021 |
, Press Release | Optimus announces Interim Clinical Results from Phase III Clinical Trials of Molnupiravir conducted in India |
| 58% improved viral clearance (p<0.0001). Interim report on CTRI/2021/06/033992, showing faster viral clearance. Event counts are approximate, the press release only provides percentages. | ||
Jul 9 2021 |
, Press Release | Hetero Announces Interim Clinical Results from Phase III Clinical Trials of Molnupiravir conducted in India |
| 70% lower hospitalization (p=0.003) and 33% faster recovery (p=0.0001). Interim results for CTRI/2021/05/033739, showing lower mortality and faster recovery. | ||
Jul 9 2021 |
et al., The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab361 | Molnupiravir Inhibits Replication of the Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern in a Hamster Infection Model |
| Hamster study showing molnupiravir effective against the original, B.1.1.7, and B.1.351 variants. | ||
Jun 18 2021 |
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.06.17.21258639 | Molnupiravir, an Oral Antiviral Treatment for COVID-19 |
| 77% lower mortality (p=0.31) and 49% improved viral clearance (p=0.12). RCT 202 outpatients in the USA showing significantly faster viral clearance, but no significant differences in symptom duration or severity. NCT04405570. | ||
May 7 2021 |
et al., The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab247 | β-D-N4-hydroxycytidine Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Through Lethal Mutagenesis But Is Also Mutagenic To Mammalian Cells |
| In Vitro study showing that NHC (initial metabolite of molnupiravir) has high antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2, but also shows host mutational activity in an animal cell culture assay. Authors note the concern that mutations in host .. | ||
Apr 15 2021 |
, News Release | Merck and Ridgeback Biotherapeutics Provide Update on Progress of Clinical Development Program for Molnupiravir, an Investigational Oral Therapeutic for the Treatment of Mild-to-Moderate COVID-19 |
| News release reporting that the trial of molnupiravir with hospitalized patients (NCT04575584) has been discontinued because data indicates it is unlikely to demonstrate a clinical benefit in hospitalized patients. Results are not availab.. | ||
Please send us corrections, updates, or comments.
c19early involves the extraction of 100,000+ datapoints from
thousands of papers. Community updates
help ensure high accuracy.
Treatments and other interventions are complementary.
All practical, effective, and safe
means should be used based on risk/benefit analysis.
No treatment or intervention is 100% available and effective for all current
and future variants.
We do not provide medical advice. Before taking any medication,
consult a qualified physician who can provide personalized advice and details
of risks and benefits based on your medical history and situation. FLCCC and WCH
provide treatment protocols.
Thanks for your feedback! Please search before submitting papers and note
that studies are listed under the date they were first available, which may be
the date of an earlier preprint.